On This Day in Tech History
Stories Published|June 24|Throughout History
Historic Tech Events

The First Eurovision Song Contest Was Held
1956Switzerland hosted the very first song contest, spawning an annual series that initially began as an experiment in live television broadcasting. Swiss singer Lys Assia won the very first iteration of the competition.
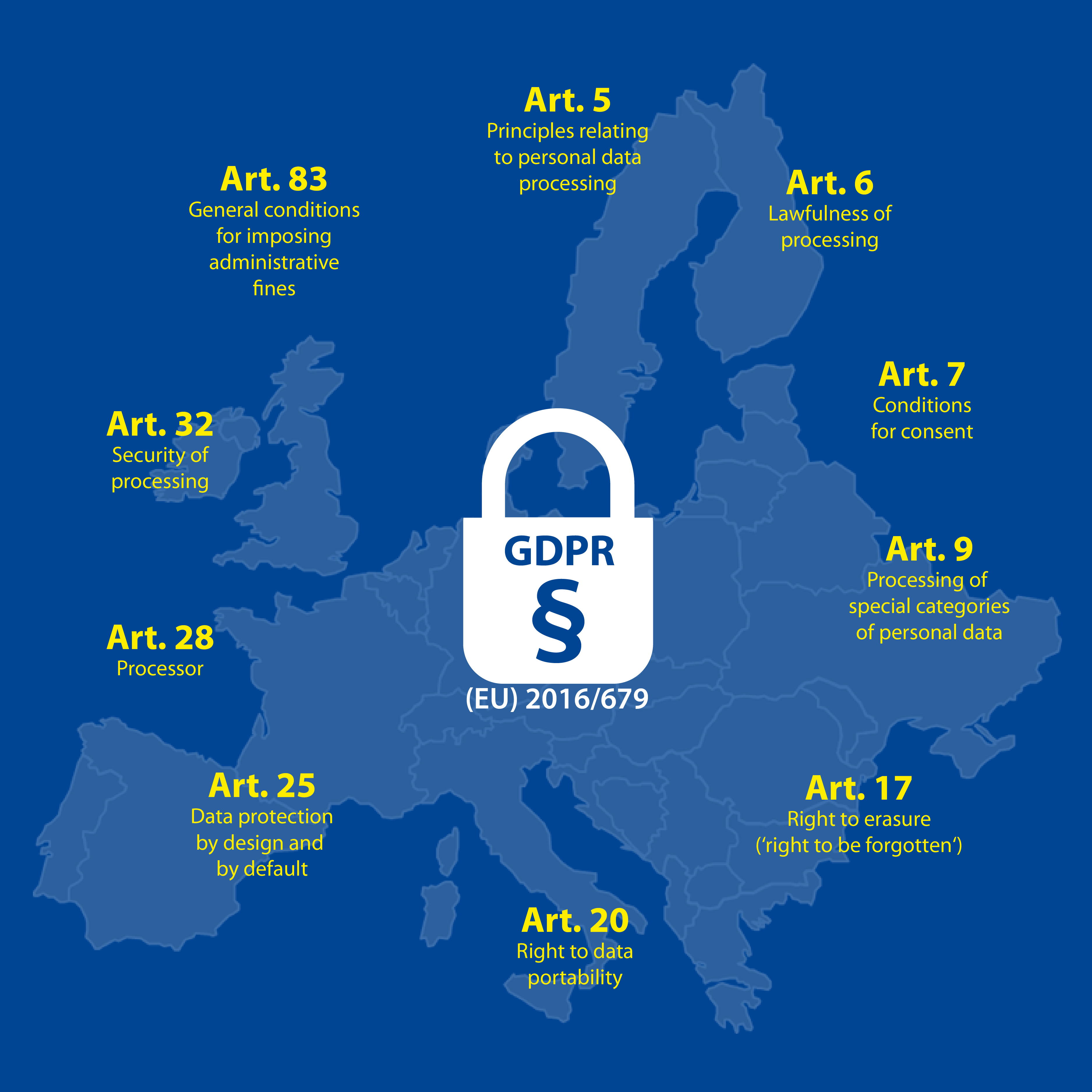
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) Came Into Effect
2016The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) introduced strict regulations on data protection and privacy for individuals within the EU and the European Economic Area (EEA). It set out strict rules on how companies handling personal data must protect it, and gave individuals more control over their personal data.

The Brooklyn Bridge Opened
1883The 486.3 meter bridge opened over 13 years after construction began and cost nearly half a billion in 2023 dollars.
Stories Published in 2025
Stories Published in 2024
Stories Published in 2023
Stories Published in 2022
Stories Published in 2021
Stories Published in 2020
Stories Published in 2019
Stories Published in 2018
Stories Published in 2017
Stories Published in 2016