On This Day in Tech History
Stories Published|June 21|Throughout History
Historic Tech Events

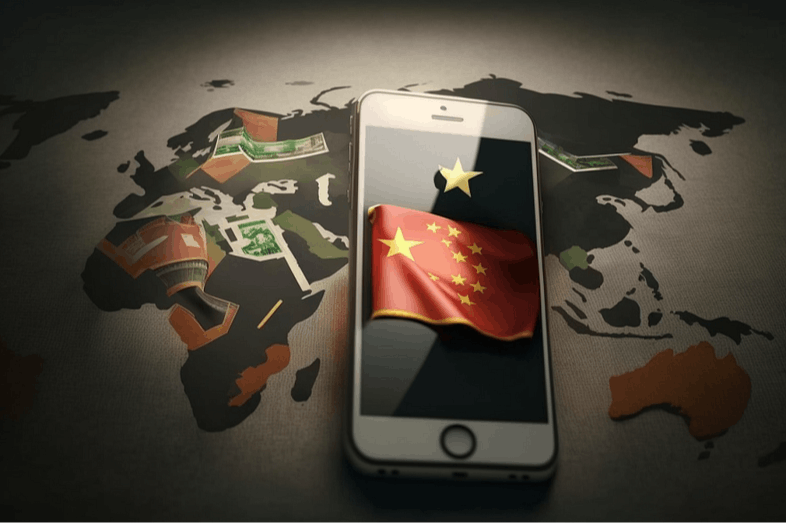
Huawei was placed on the U.S. Entity List
2019Huawei was placed on the U.S. Entity List, effectively banning American companies from doing business with the Chinese tech giant due to national security concerns.

Charles Lindbergh Completed the First Solo Nonstop Transatlantic Flight
1927Charles Lindbergh landed in Paris after beginning his journey from New York a day earlier. The 33.5 hour-flight helped demonstrate advancements in aviation technology at the time.

FIFA Was Founded
1904The governing body of one of the most popular sports in the world was formed today! Not only does FIFA regulate Football, it also oversees beach soccer and futsal.
Stories Published in 2025
Stories Published in 2024
Stories Published in 2023
Stories Published in 2022
Stories Published in 2021
Stories Published in 2020
Stories Published in 2019
Stories Published in 2018
Stories Published in 2017
The Hydra Bug: Part II
May 21, 2017