91,705 reads
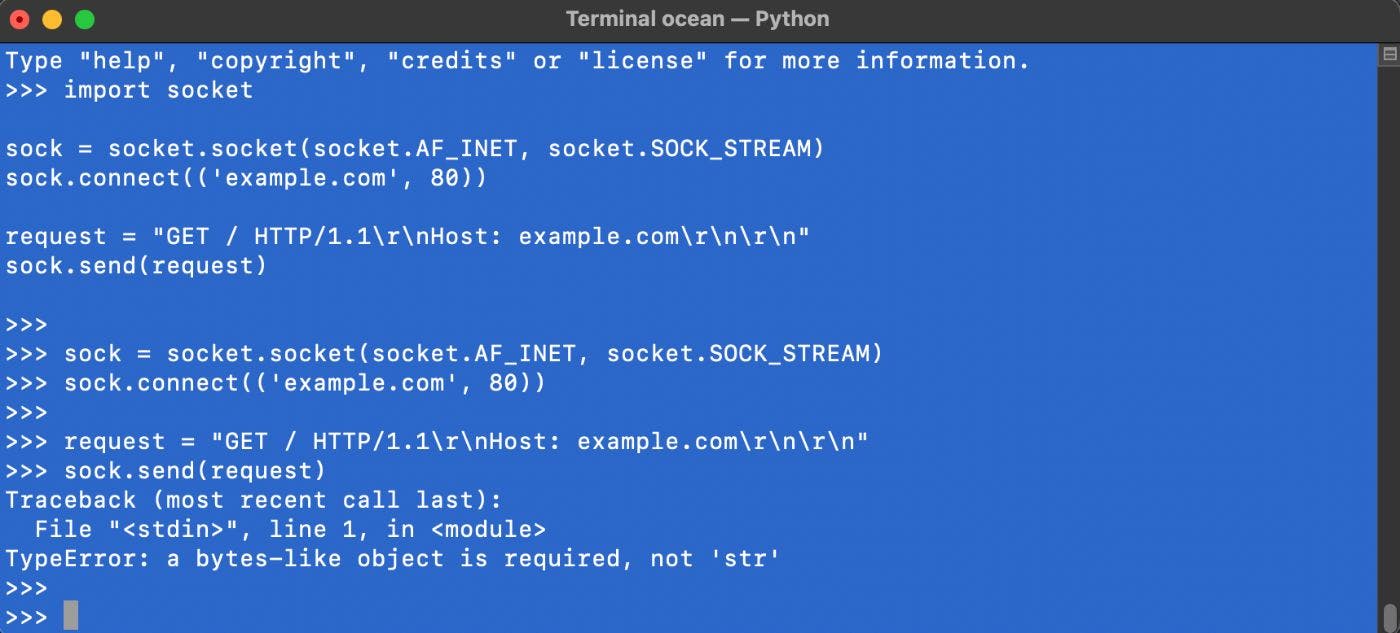
Resolving TypeError: A Bytes-like Object is Required, Not 'str' in Python
by
April 6th, 2023
Audio Presented by
Vinish is a blogger, author, and frequent speaker at various conferences and seminars.
About Author
Vinish is a blogger, author, and frequent speaker at various conferences and seminars.