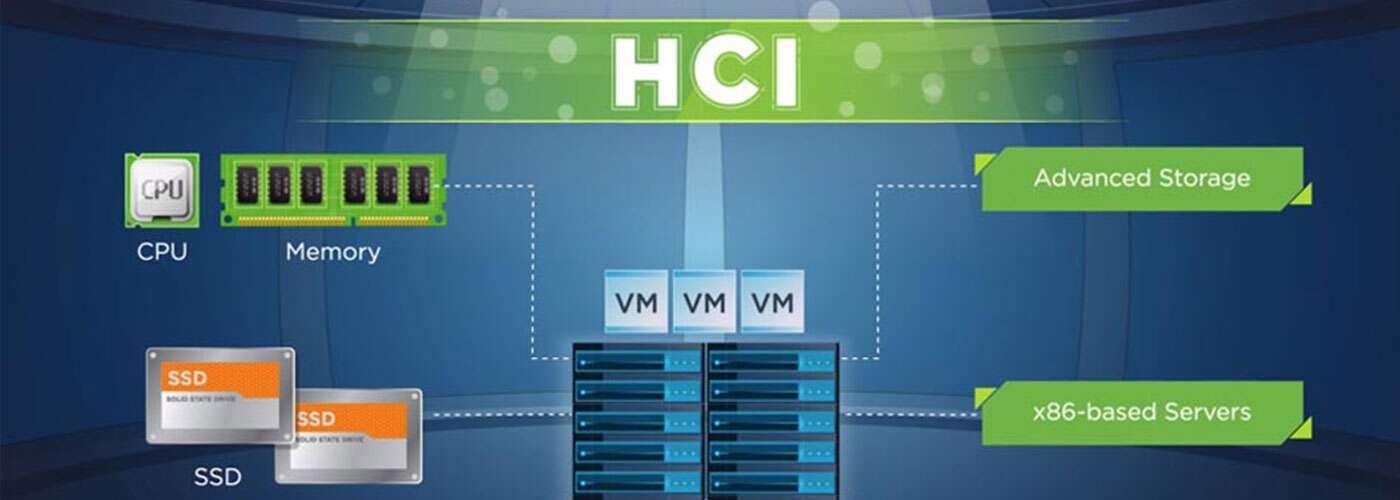
Hyper Converged Infrastructure: 'All the Eyes in One Basket'
by
February 13th, 2022
Audio Presented by

Atiq Malik is a technology web content creator and a cloud computing enthusiast working with cloud computing.
About Author
Atiq Malik is a technology web content creator and a cloud computing enthusiast working with cloud computing.