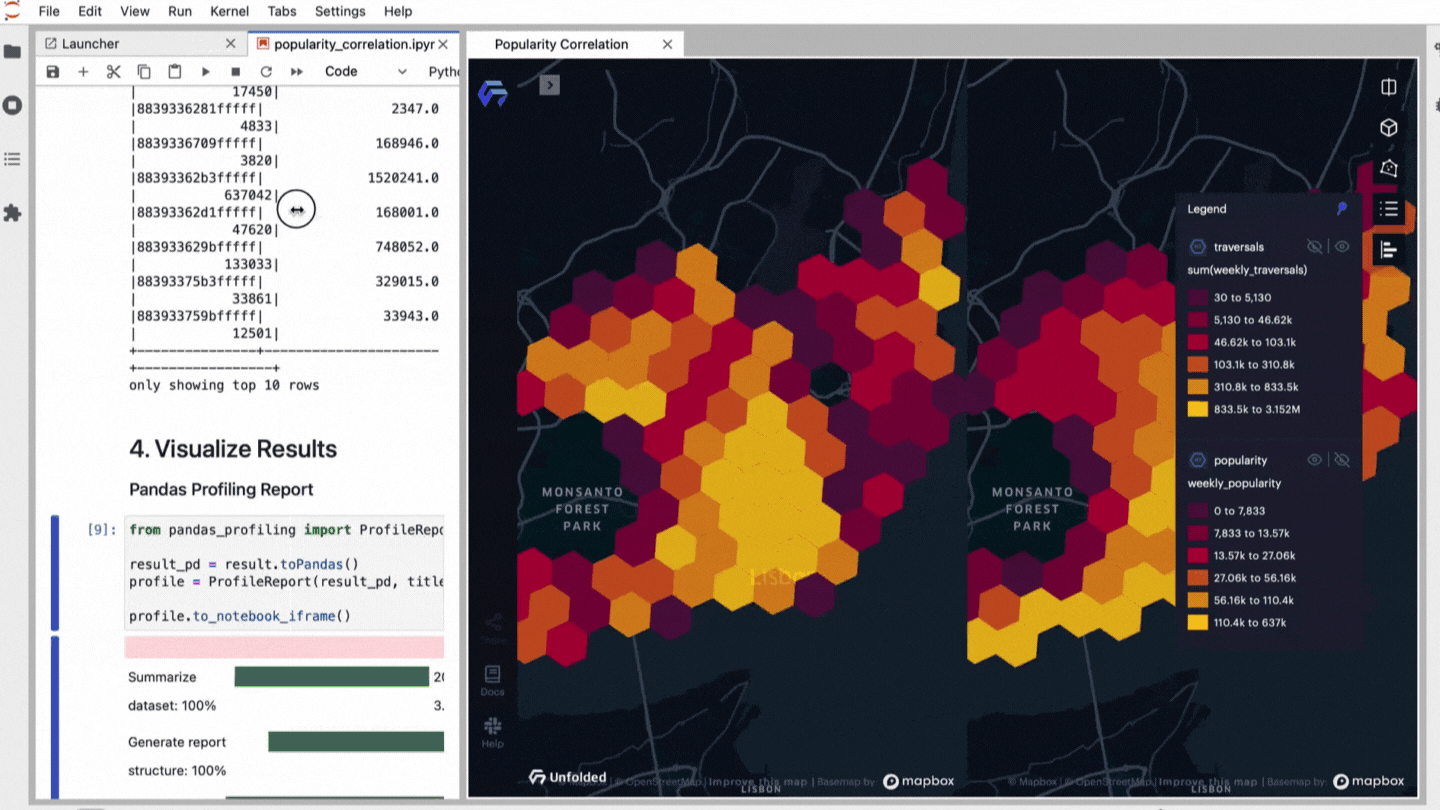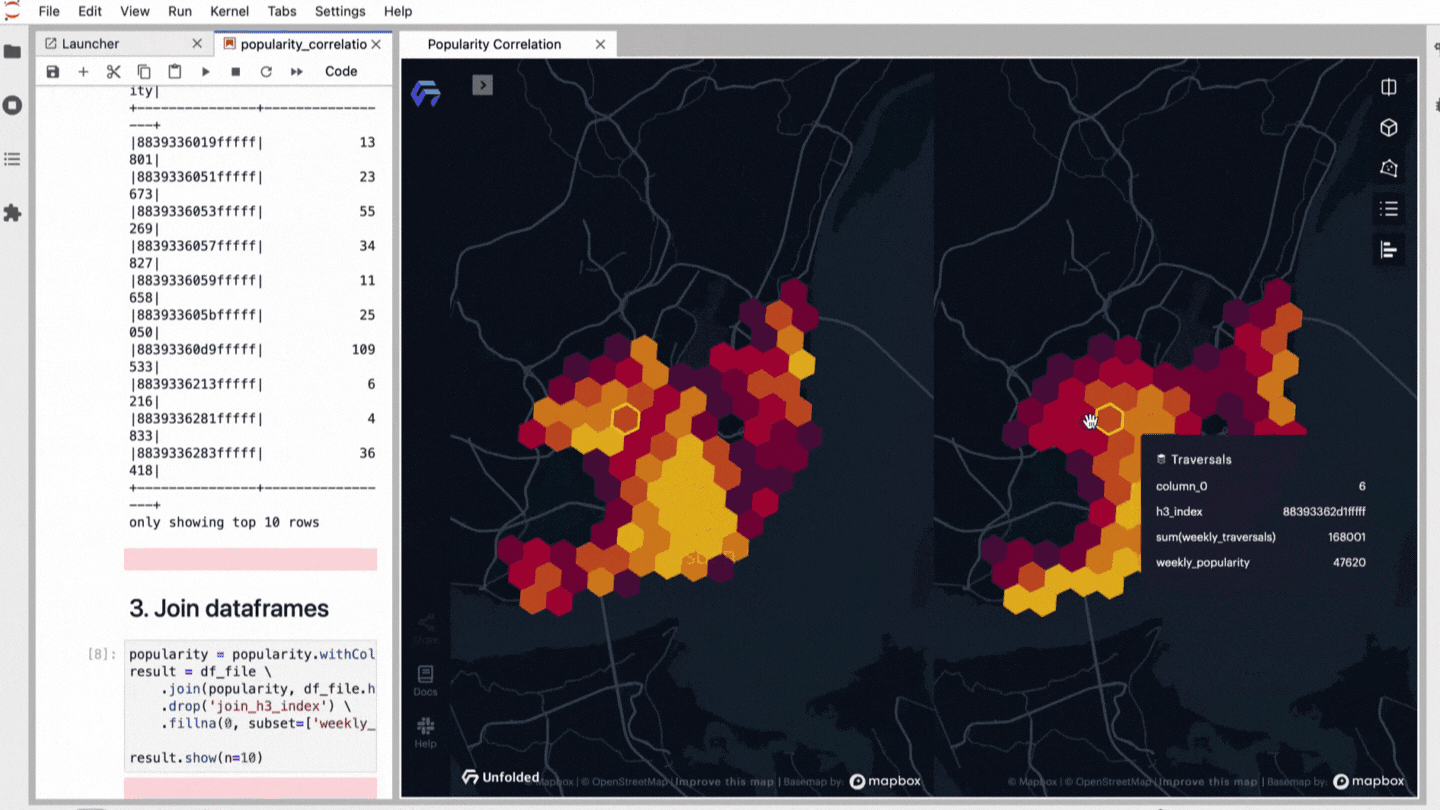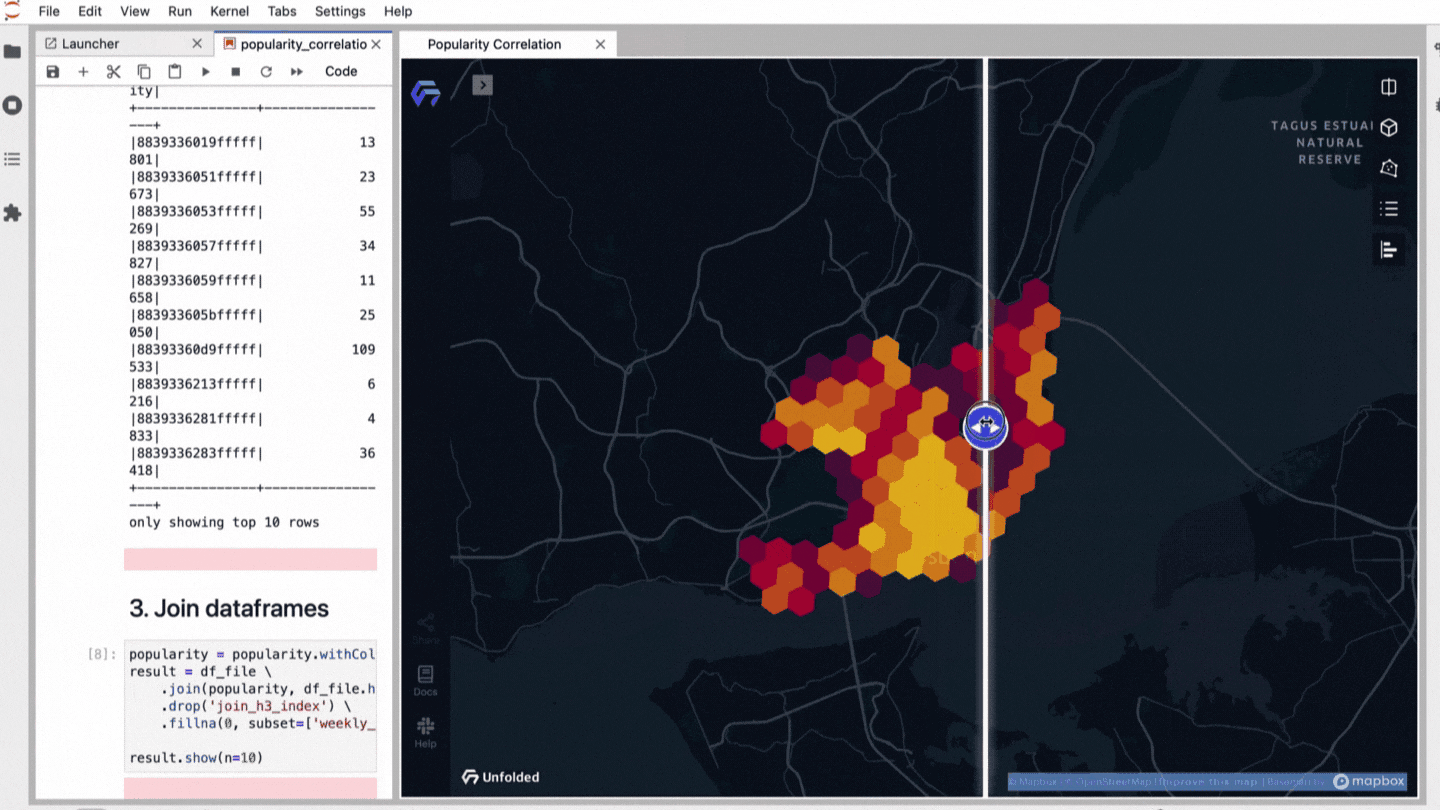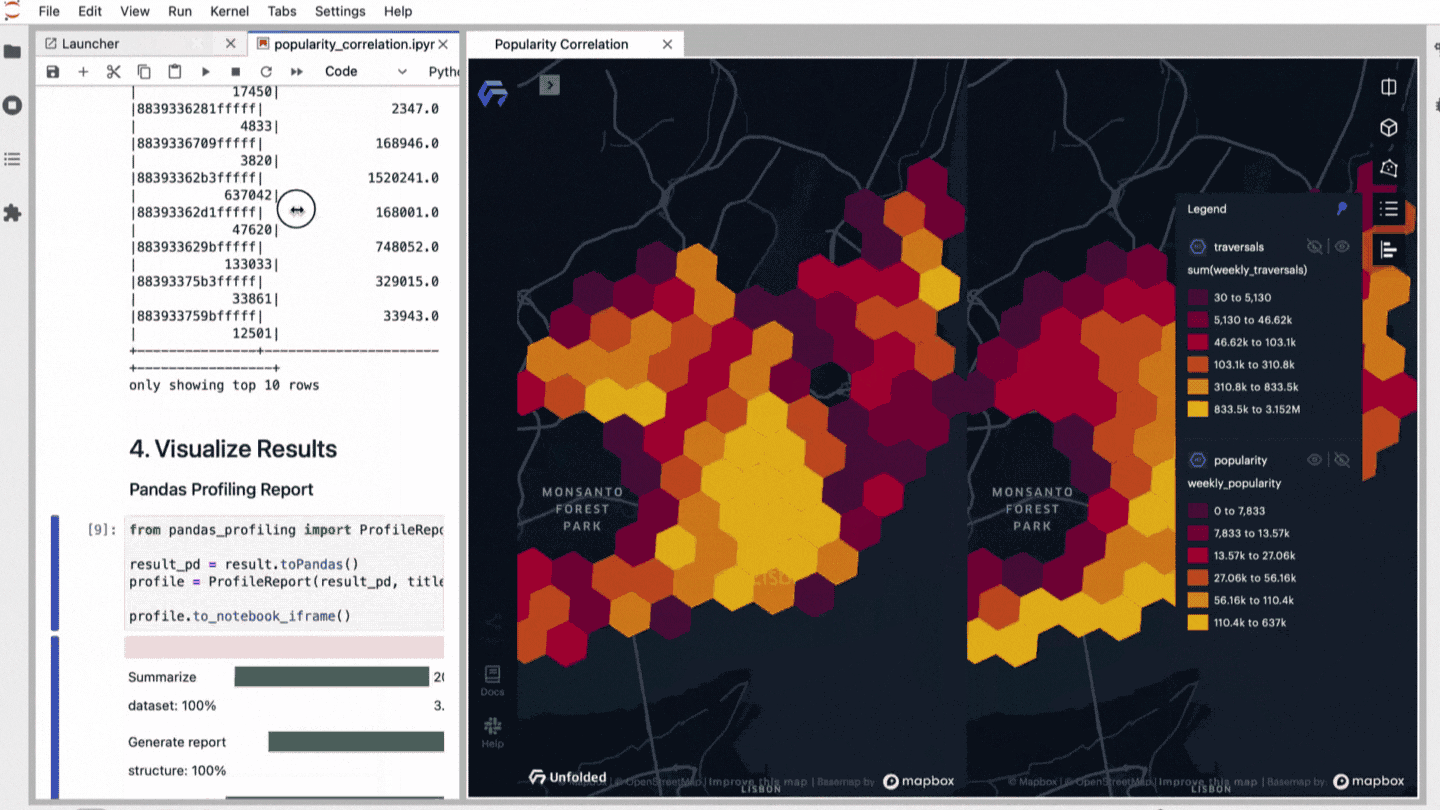
115 reads
How to Build an Uber-like Intelligence System for a Mobility Startup
by
November 5th, 2021
Audio Presented by

Kuwala is an Open Source No Code Data Platform that reduces the friction between BI Analysts and Engineers.
About Author
Kuwala is an Open Source No Code Data Platform that reduces the friction between BI Analysts and Engineers.