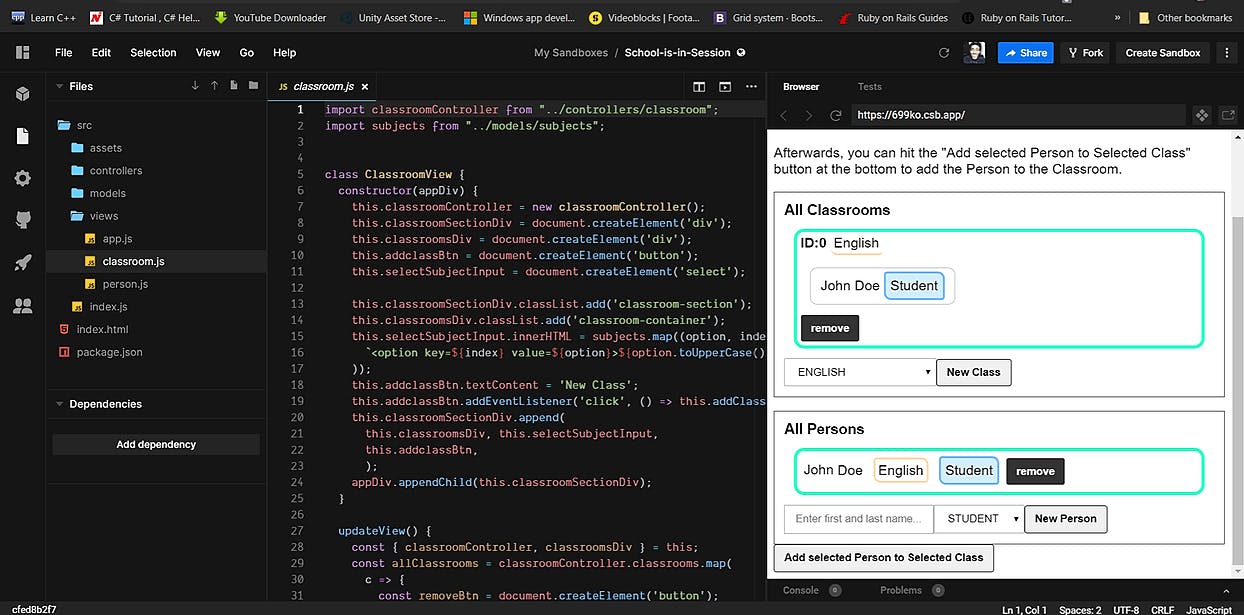
667 reads
How I Adopted the Model, View, Controller (MVC) Architectural Pattern in JavaScript
by
May 19th, 2020

Full-Stack Developer - JavaScript, React, Ruby, Rails. Portfolio: https://aaronrory.com
About Author
Full-Stack Developer - JavaScript, React, Ruby, Rails. Portfolio: https://aaronrory.com