3,250 reads
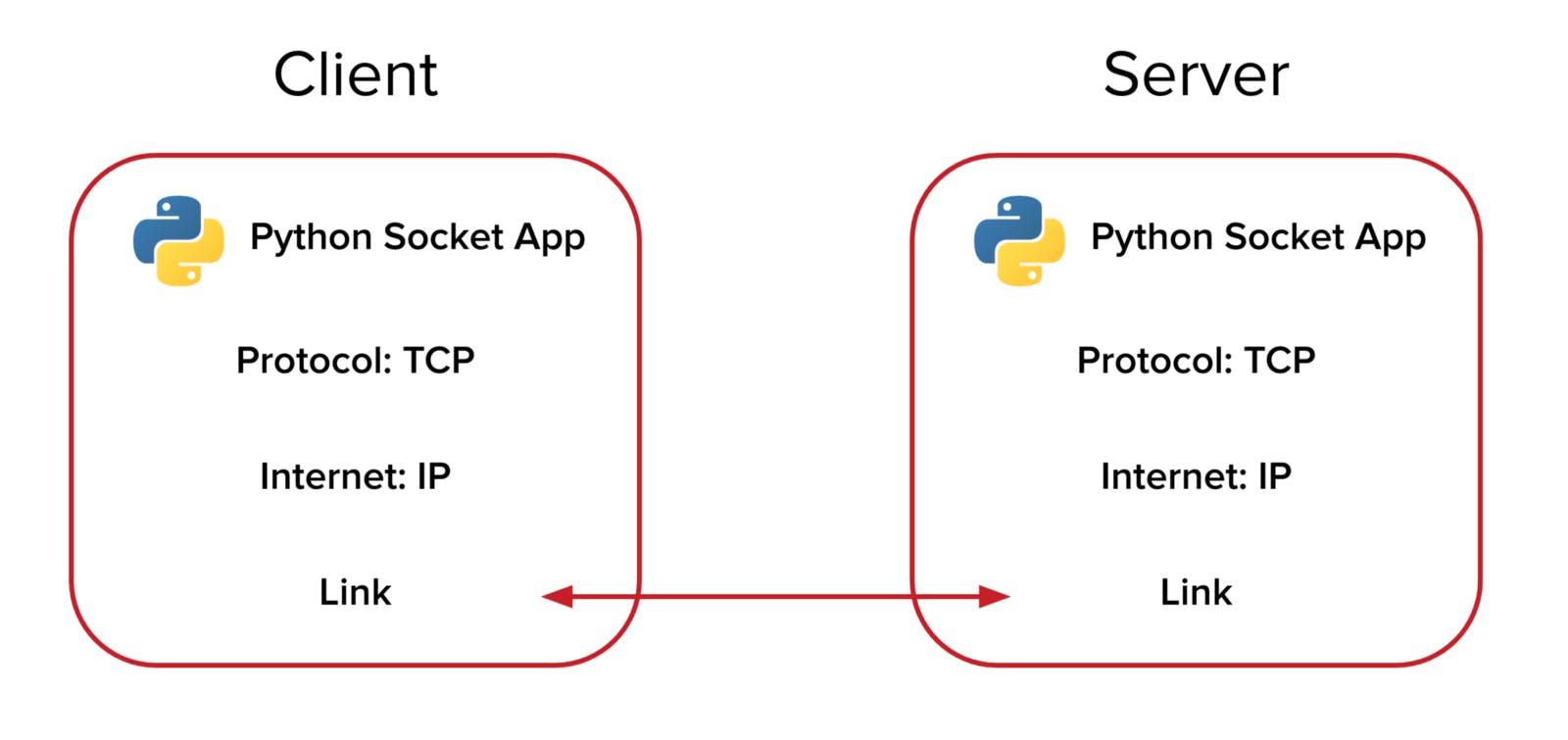
Socket Programming in Python: Client, Server, and Peer Examples
by
January 22nd, 2019
Audio Presented by
About Author
Open Source Software Engineer
Comments
TOPICS
THIS ARTICLE WAS FEATURED IN
Related Stories
Bitcoin at 10
Apr 26, 2018
Bitcoin at 10
Apr 26, 2018