8,592 reads
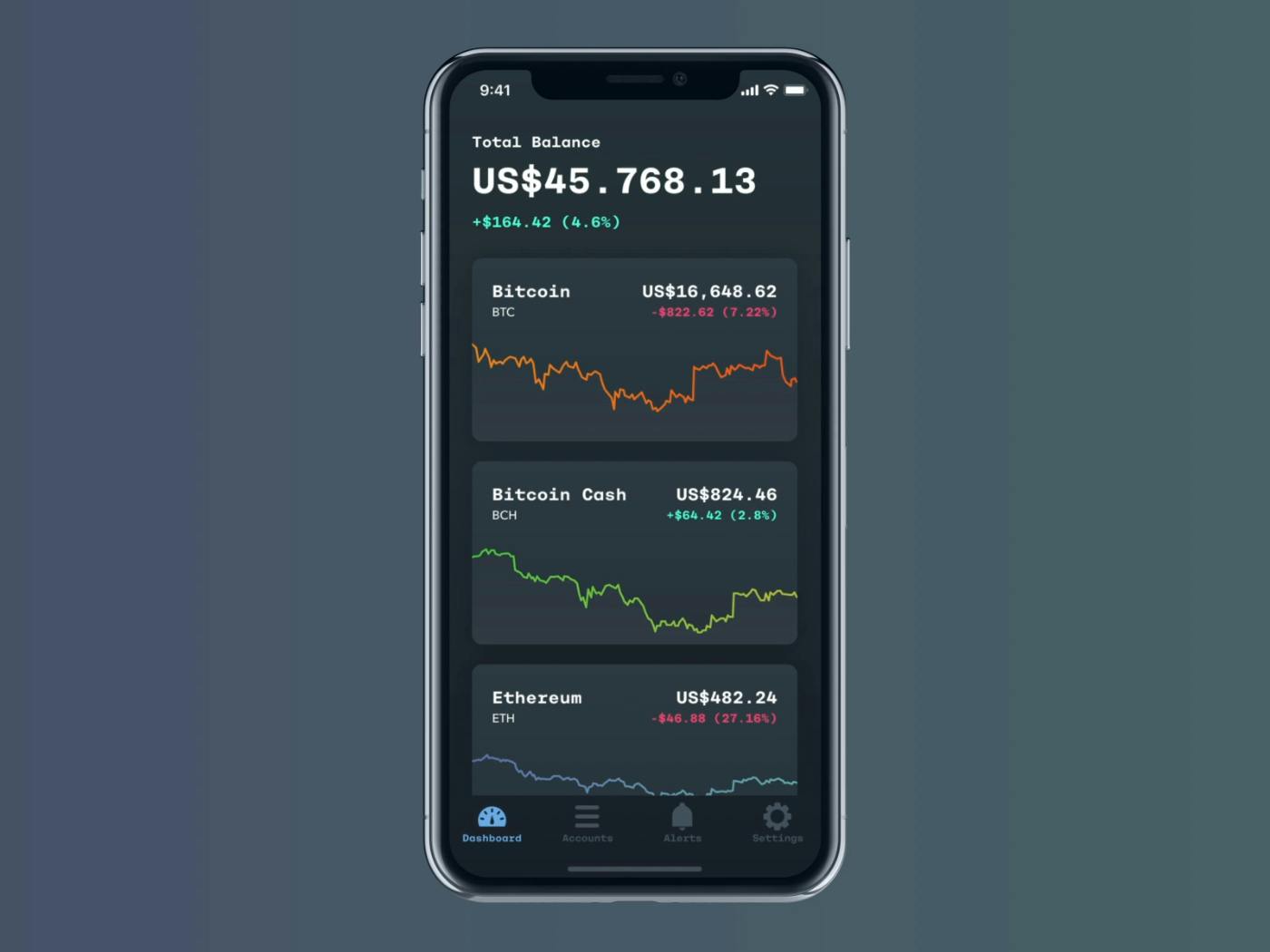
How to Build Your Own Crypto Trading App: A Step-by-Step Tutorial
by
December 6th, 2023
Audio Presented by
Story's Credibility

About Author
Hi I'm Imisioluwa, A Developer and writer.
Comments
TOPICS
Related Stories
10 Threats to an Open API Ecosystem
Jul 18, 2022